Why Is Culturally and Linguistically Competent Care Important in Stark County?
Culturally and Linguistically Competent Care in Stark County will (1) aim to eliminate or reduce cultural, racial, ethnic or geographical disparities as well as (2) eliminate barriers to services and increase access, quality and outcomes for underserved populations. Efficient and relevant services for all of Stark County generate better outcomes and avoid inappropriately and/or inadequately serving Stark County’s underserved populations. Culturally and linguistically appropriate services are respectful of and responsive to individual cultural health beliefs and practices, preferred languages, health literacy levels and communication needs and employed by all members of an organization at every point of contact.
Understanding Cultural & Linguistic Competence
Cultural Competence is a set of values and principles that are reflected within the behaviors, attitudes, policies and structures of agencies, family/youth organizations, providers and community stakeholders to result in appropriate and effective services for all.
Linguistic Competence is the capacity of personnel to communicate effectively and convey information in a manner that is easily understood by diverse audiences. Linguistic Competence involves the development of interagency and internal capacity to respond effectively to the mental health literacy and communication needs of the populations served, and to possess the policy, structures, practices, procedures and dedicated resources to support this capacity.
Source: Adapted from Cross T., Bazron, B., Dennis, K., & Isaacs, M. (1989)
Four Components of Cultural Competence
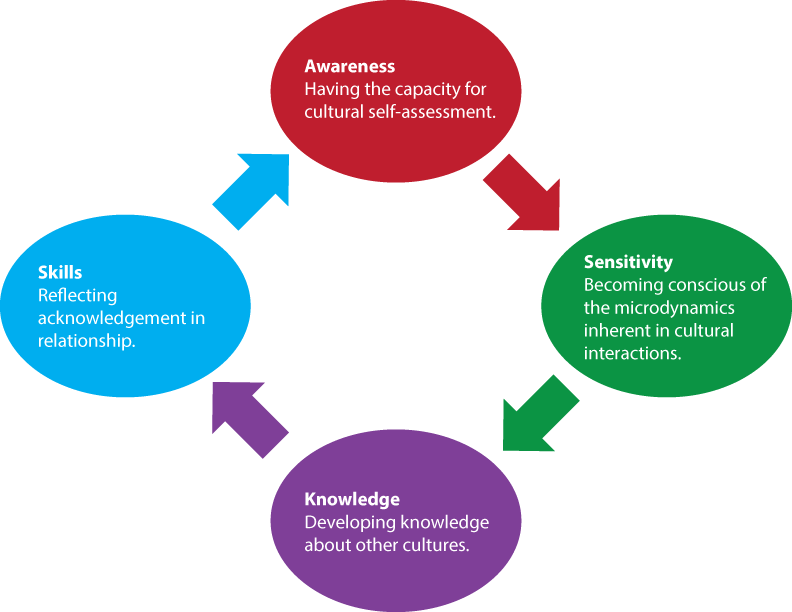
- Awareness: Having the capacity for cultural self-assessment
- Sensitivity: Becoming conscious of the microdynamics inherent in cultural interactions
- Knowledge: Developing knowledge about other cultures
- Skills: Reflecting acknowledgment in Relationship
Source: http://www.ecald.com/Courses, accessed Oct. 8, 2015
Six Domains of Cultural and Linguistic Competence
- Governance and organizational infrastructure
- Services and supports
- Planning and continuous quality improvements
- Collaboration
- Communication
- Workforce development
Source: http://www.tapartnership.org/COP/CLC/implementationGuide.php, accessed Oct. 8, 2015
Cultural Competence and CLAS Standards
*CLAS standards have been adopted by the Office of Health and Human Services – Office of Minority Health. Additional information and resources on Cultural Competence can be found on the following websites:
Office of Minority Health
View the Inclusion Tool Kit
The Cultural Influences and Health Care Series Inclusion Tool Kit is available online! Click the links below to view each section.
Tool Kit Binder Part I
Tool Kit Binder Part II
- Faith-Based Culture and Community »
- Amish Culture and Community »
- Cultural Perspectives on Trauma »
- Transgender Culture and Community »
- New American Culture and Community »
- Mayan Culture and Community Video »
- Asian Culture and Community Video »
- Deaf Culture and Community Video »
- Unconscious Bias Video »
For training questions, please contact the Training Coordinator, at 330-455-6644.
